What Is the Staffing Industry?
Staffing is a growing industry, full of opportunity and challenge. It has expanded vastly from a narrow sector known for providing “temps” to fill in for sick or vacationing workers. Today, staffing is an all-encompassing industry providing a full range of human resource services to virtually every type of business and employer across the globe.
State of the Industry: Broad-Based Growth
Staffing Industry Analysts expects staffing industry growth in 2022 in the United States to total 14%, with total revenue at a record $212.8 billion. Growth has been across all segments of staffing; estimates are office/clerical (+7%), industrial (+10%), IT (+16%), and healthcare (+18%) skill segments.
As of August 2022, the U.S. temporary staffing industry accounted for 3.162 million jobs, 2.1% of the U.S. workforce.
Source: US Staffing Industry Forecast: September 2022 Update
Global Revenue Growth
Figures for 2021, the most recent annual numbers calculated, indicate global staffing revenue increased by 23% to generate USD 620 billion in global revenue, according to Staffing Industry Analysts. The U.S., Japan and the UK accounting for 53% of the total revenue. Healthcare staffing has been a strong driver of market growth over this period.
The Workforce Solutions Ecosystem
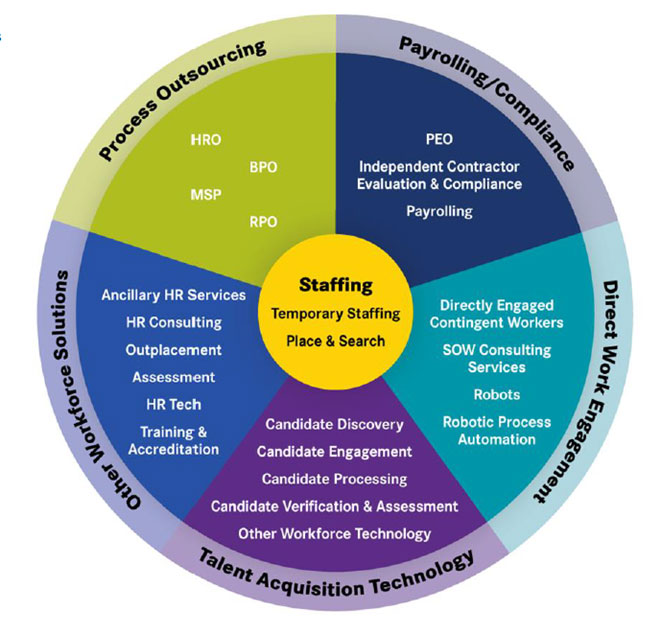 Staffing Industry Analysts, a global advisor on staffing and workforce solutions, coined the term “Workforce Solutions Ecosystem,” which describes the many facets of the staffing industry. It is comprised of six primary industry segments: Staffing, Process Outsourcing, Payrolling/Compliance, Direct Work Engagement, Talent Acquisition Technology, and other Workforce Solutions.
Staffing Industry Analysts, a global advisor on staffing and workforce solutions, coined the term “Workforce Solutions Ecosystem,” which describes the many facets of the staffing industry. It is comprised of six primary industry segments: Staffing, Process Outsourcing, Payrolling/Compliance, Direct Work Engagement, Talent Acquisition Technology, and other Workforce Solutions.
The staffing industry is at the core of this Ecosystem.
As the industry has evolved, so has MeeDerby’s reach. We work with companies across the workforce solutions ecosystem and the people who specialize in it. Have questions about hiring in the workforce solutions ecosystem? Give us a call!
Staffing Industry Segments
Temporary Staffing
The largest segment of the industry and the most well-known is temporary staffing, a frequent source of on-demand hiring for short- and long-term assignments. Staffing Industry Analysts categorizes the following occupational verticals: 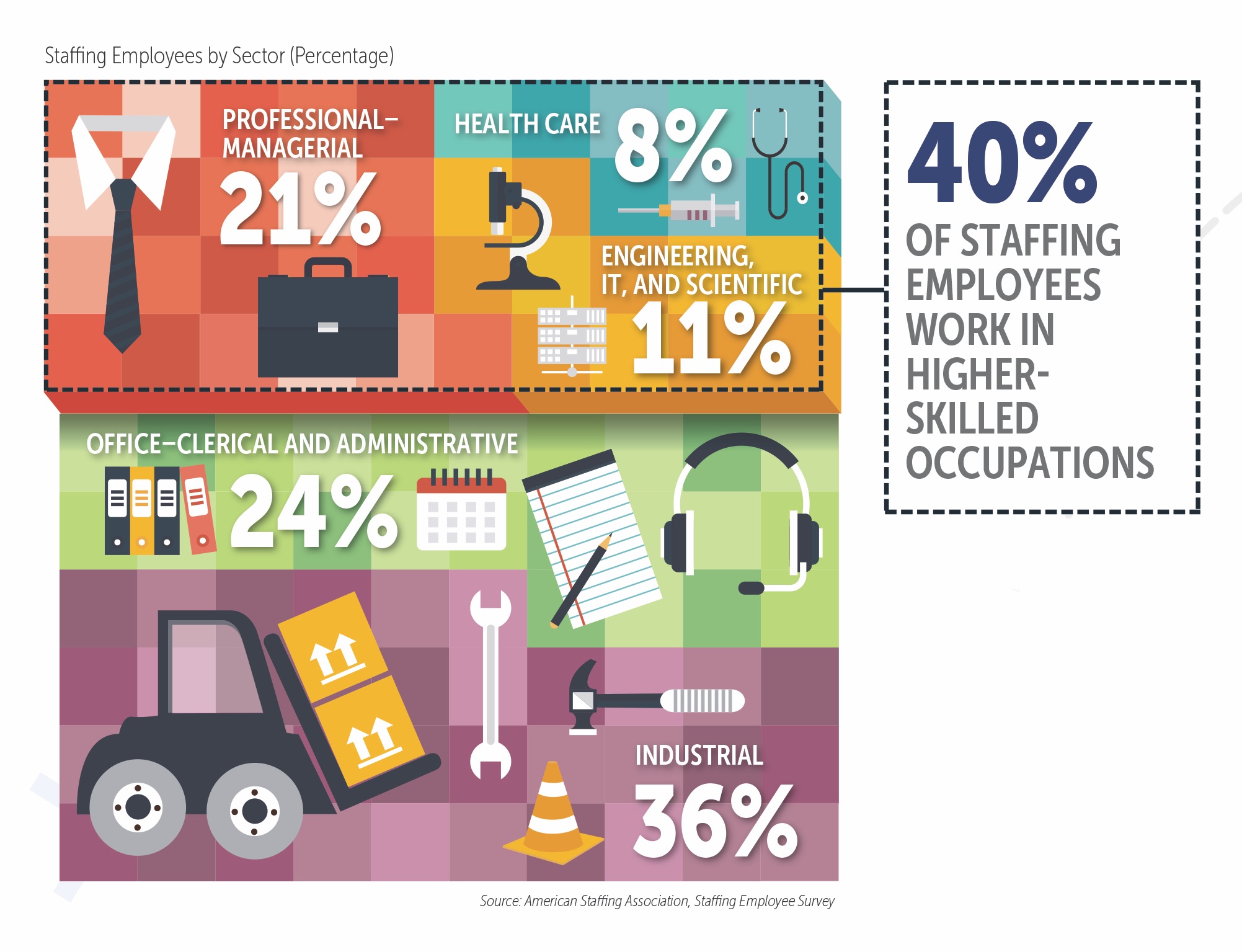
- Office/Clerical
- Industrial
- Information Technology
- Healthcare
- Finance/Accounting
- Engineering
- Legal
- Life Sciences
- Clinical/Scientific
- Marketing/Creative
- Education
How it Works
Temporary staffing firms recruit, screen, often train, and assign their employees to work at client companies on an as-needed basis. The staffing firm retains its position as employer of record and is responsible for paying the temporary employees, handling any tax, insurance and benefit requirements. Clients are charged an hourly rate for each employee.
For larger employers, staffing firms may provide an on-site manager to manage the large temporary workforce at the customer’s facility. This is referred to as vendor-on-premise (VOP).
Some larger companies will also work with a managed service provider (MSP) that will take responsibility for managing the company’s contingent staffing buy and relationship with various staffing vendors. They may manage this process through managed service agreements, which also provide performance metrics and measurements.
Temp-to-hire staffing provides a means for employers to try an employee on-site to assess their skills and fit before committing to a full-time hire.
Search
This is a smaller segment of the staffing sector, but one with significant impact. Search firms find full-time employees for their clients, and take responsibility for sourcing, recruiting, screening, interviewing and matching potential candidates for a client company’s full-time job openings.
Search options
- Retained Search. Client company pays a predetermined fee for the search firm to identify and interview for executive-level positions. This model requires significant consulting time and resources to identify the right candidates. This exclusive search fee is typically paid in thirds: at the signing of the contract, upon submission of a short list of candidates, and when a candidate is hired.
- Engaged Search. A search is conducted to find qualified candidates to fill open jobs and charges a portion of the placement fee as a retainer. The balance is due once the hire is made. Engaged searches are best for higher-level positions or hard-to-fill jobs that require more in-depth research and considerable resources.
- Contingent Search. The search firm is only paid upon the successful hiring of a candidate. This “pay for performance” model provides access to top talent, but no fee until the hire is made.
Fees are typically a percentage of the candidate’s salary, although the fee schedule for retained search can be structured in a variety of ways to accommodate the client.
The Rise of Staffing Technology
Another development in staffing that bears watching is the increase in the number and usage of platforms that assist the industry or compete with it.
Temporary staffing platforms automate tasks involved with provisioning temporary employees, getting them to work faster with fewer speed bumps. These platforms are gaining a foothold in sectors like light industrial which require large staffing volumes.
Talent acquisition platforms streamline and automate the various tasks associated with the hiring process, including recruitment, engagement, assessment, and verification.
Talent platforms (excluding those like Uber, Lyft and DoorDash) generated $13.8 billion in 2021. Temporary staffing platforms earned nearly the same, increasing the total spend on these B2B platforms to $26 billion globally.
Outlook for 2023: Limited Growth in Some Sectors
Looking ahead to 2023, SIA predicts the U.S. staffing industry will grow 2% and reach a record $216.8 billion. Without the travel nurse segment, which is expected to decline from its 2022 peak, overall growth could be 6%. In 2023, the staffing segments expected to grow include industrial (+5%), IT (+8%), finance/accounting (+7%), and engineering (+5%).
Factors Leading To Uncertainty for 2023
- GDP growth projected to be only 0.2%
- The staffing industry will be impacted by persistent inflation, rising interest rates, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions.
- Ongoing and unpredictable emergence of new virulent Covid variants.
- Inflation in pay rates and bill rates.
Source: US Staffing Industry Forecast: September 2022 Update
Are you interested in joining the staffing industry?
Are you looking to transition into the staffing industry? If so, here are some resources to help you. MeeDerby only places professionals with staffing industry experience, but there are other companies that will consider those without staffing industry experience.
Here is a list of companies that offer internship programs or management training programs. You can contact them directly for more information.
Choose Staffing as a Career and Love What You Do










